2025年陕西省普通高等学校艺术类专业招生考试说明
2025年的陕西艺考主要分为两个阶段:省级统考(联考)和校考。
第一部分:省级统考(全省艺术类专业课统一考试)
省级统考是陕西省对所有艺术类考生进行的统一专业水平测试,是考生参加校考和被艺术类本科专业录取的重要资格,2025年,陕西省组织的省级统考专业包括:
- 美术类
- 音乐类
- 舞蹈类
- 播音编导类
重要提示: 2025年,陕西省没有组织表演类、播音主持类(不含编导)和书法类的省级统考,这些专业的考生通常需要直接参加招生院校组织的校考。
第二部分:各统考类专业具体说明
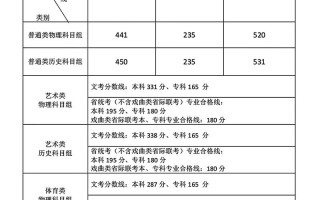
美术类专业
-
考试科目(共3科,总分300分):
- 素描(100分)
- 静物、石膏像或人物头像。
- 要求: 考查考生对造型、光影、结构、空间的理解和表现能力,要求构图完整、比例准确、刻画深入、画面整体。
- 色彩(100分)
- 静物(通常为水果、蔬菜、花卉、衬布等组合)。
- 要求: 考查考生的色彩感知、色彩关系运用和画面塑造能力,要求色调明确、色彩和谐、塑造充分、空间感强。
- 速写(100分)
- 人物动态(通常为单人或双人组合)。
- 要求: 考查考生对人物动态、比例、结构的把握以及快速表现能力,要求动态生动、比例准确、线条流畅。
- 素描(100分)
-
考试形式: 全部为现场写生。
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删) -
考试时间: 通常在每年12月底至次年1月初进行,具体时间由陕西省教育考试院公布。
音乐类专业
-
考试科目(共4科,总分300分):
- 基本乐理(30分)
- 音名、唱名、音程、和弦、调式、调性、节奏、节拍、音乐术语等基础理论知识。
- 形式: 闭卷笔试。
- 视唱(60分)
- 现场抽取一条简谱乐谱进行演唱。
- 要求: 考查音准、节奏、流畅性等,通常是五线谱或简谱(当年具体要求以当年简章为准)。
- 练耳(60分)
- 听辨音程、和弦、节奏、旋律等。
- 形式: 通过播放录音,考生在试卷上写出答案。
- 主项(150分)
- 考生在声乐或器乐中选择一项作为主项进行考试。
- 要求:
- 声乐: 演唱中外歌曲1-2首,要求发声方法正确、音准节奏好、表现力强。
- 器乐: 演奏中外乐曲1-2首(除钢琴外,其他乐器自备),要求演奏技巧娴熟、音乐表现力好。
- 基本乐理(30分)
-
考试形式: 笔试(乐理、视唱、练耳)和现场面试(主项)相结合。
-
考试时间: 通常在每年1月下旬至2月上旬进行。
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)
舞蹈类专业
-
考试科目(共4科,总分300分):
- 基本条件测试(100分)
- 身高、体重比例测量;软开度(横叉、竖叉、下腰等);弹跳能力(小跳、中跳等)。
- 要求: 考查考生的身体基本条件、柔韧性和爆发力。
- 舞蹈表演(150分)
- 考生自备一个舞蹈剧目(时长通常在2-3分钟)进行表演。
- 要求: 舞种不限(古典舞、民族民间舞、芭蕾舞、现代舞等),要求技术技巧熟练、情感表现力强、台风好。
- 动作模仿(50分)
- 考官现场示范一组舞蹈动作,考生进行模仿。
- 要求: 考查考生的协调性、记忆力和快速学习能力。
- 基本条件测试(100分)
-
考试形式: 现场面试。
-
考试时间: 通常在每年1月下旬至2月上旬进行。
播音编导类专业
-
考试科目(共3科,总分300分):
- 基本素质与专业知识(笔试,100分)
- 涵盖文学、艺术、文化、时事政治、新闻传播、广播电视常识等。
- 形式: 选择题、填空题、简答题等。
- 新闻播报与稿件播读(面试,100分)
- 现场抽取新闻稿件进行播报。
- 要求: 考查普通话语音面貌、发声技巧、语感、新闻感和对象感。
- 作品分析(笔试,100分)
- 观看一部指定的电视短片或电影片段,并在规定时间内撰写一篇分析评论文章。
- 要求: 考查考生的视听分析能力、逻辑思维能力和文字表达能力。
- 基本素质与专业知识(笔试,100分)
-
考试形式: 笔试和面试相结合。
-
考试时间: 通常在每年1月下旬至2月上旬进行。
第三部分:校考
- 报名资格: 考生必须先参加陕西省的省级统考并合格(美术类、音乐类、舞蹈类、播音编导类),才有资格参加省内外院校组织的相应专业校考,对于未组织省级统考的专业(如表演类),考生可直接报名参加相关院校的校考。
- 招生院校: 包括独立设置的艺术院校、参照独立设置艺术院校招生办法执行的院校,以及省内外其他有艺术类招生计划的普通高校。
- 报名方式: 考生需登录陕西招生考试信息网或目标院校的招生网站,按照院校的要求进行报名、缴费和打印准考证。
- 由各招生院校自行确定,考试内容和形式更加多样,旨在选拔更符合该校专业培养目标的人才。
第四部分:文化课考试与录取
- 文化课考试: 艺术类考生必须参加全国普通高等学校招生文化课统一考试(高考)。
- 志愿填报: 艺术类考生在高考后,单独填报艺术类志愿。
- 录取原则(2025年):
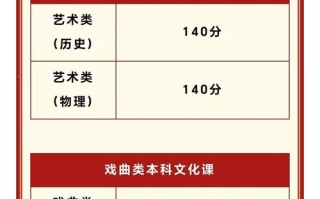
- 省级统考专业: 大部分省内院校和承认陕西统考成绩的省外院校,采用专业课成绩和文化课成绩(高考总分)按一定比例折算后形成的综合分从高到低择优录取。
- 校考专业: 由招生院校自行制定录取办法,常见的有:
- 文化过线,专业排名: 文化课达到最低控制线后,按专业课成绩从高到低录取。
- 专业过线,文化排名: 专业课合格后,按文化课成绩从高到低录取。
- 综合分录取: 文化课和专业课按一定比例折算成综合分,从高到低录取。
与现在的对比(重要更新)
了解2025年的情况后,也需要知道陕西艺考近年来的一些重大变化,避免信息过时:
-
新增省级统考类别:
- 书法类: 陕西省自2025年起正式组织书法类省级统考,2025年没有此类别。
- 播音主持类: 自2025年起,陕西省将原来的“播音编导类”拆分为“播音主持类”和“编导类”两个独立的统考类别,2025年的“播音编导类”包含了两者。
-
部分专业类别调整:
- 表演类: 自2025年起,陕西省也组织了表演类省级统考,2025年考生只能通过校考报考此专业。
-
统考评分标准优化:
近年来,为了更科学地选拔人才,陕西省对部分统考的评分标准进行了细化,例如美术类考试中,对素描、色彩的评分点更加明确,更注重考生的艺术素养和创意能力,而不仅仅是技术。
-
文化课要求提高:
教育部近年来持续提高艺术类考生的文化课录取控制分数线,并鼓励高校在录取时提高文化课成绩的权重,2025年的文化课要求与现在相比相对较低。
2025年的陕西艺考说明是理解陕西艺考体系的基础,它清晰地展示了当时“统考为基础,校考为补充”的招生模式,以及各专业类别的考试科目和内容,虽然部分专业类别和录取政策在近几年有所调整,但其核心的考试逻辑和对考生基本能力的要求(如美术的造型能力、音乐的基础理论、舞蹈的身体条件、编导的文学素养)至今仍然适用。
对于正在备考的您,这份旧资料可以作为了解考试风格和题型的参考,但务必以当年陕西省教育考试院发布的最新官方文件为准。
标签: 2025陕西艺考政策变化 2025陕西艺考新规定解读 2025陕西艺考改革要点